/GettyImages-1145581060-c6f3afa5f308461cab0a77d79a51c68a.jpg) Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids that are important for cell function, tissue structure, and body regulation. Most people in the U.S. consume more protein than needed, with dietary guidelines suggesting about 6.5 ounces per day for men and about 5 ounces for women.
Proteins are large molecules made up of chains of amino acids that are important for cell function, tissue structure, and body regulation. Most people in the U.S. consume more protein than needed, with dietary guidelines suggesting about 6.5 ounces per day for men and about 5 ounces for women. A protein is a naturally occurring, extremely complex substance that consists of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. Proteins are present in all living organisms and include many essential biological compounds such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies.
A protein is a naturally occurring, extremely complex substance that consists of amino acid residues joined by peptide bonds. Proteins are present in all living organisms and include many essential biological compounds such as enzymes, hormones, and antibodies. What are proteins and what do they do? Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs.
What are proteins and what do they do? Proteins are large, complex molecules that play many critical roles in the body. They do most of the work in cells and are required for the structure, function, and regulation of the body’s tissues and organs. Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues.
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues.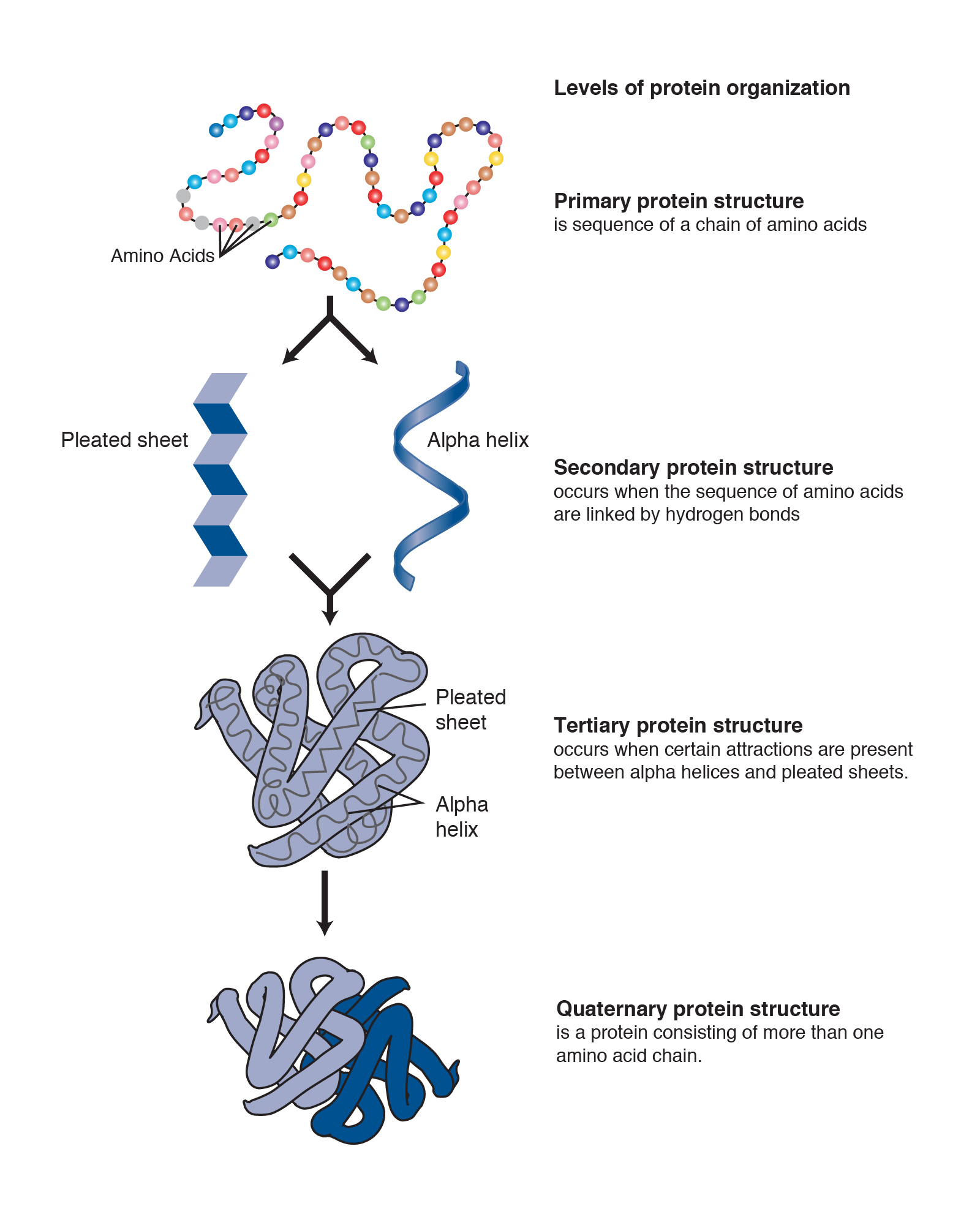 A protein is made up of one or more long, folded chains of amino acids (each called a polypeptide), whose sequences are determined by the DNA sequence of the protein-encoding gene.
A protein is made up of one or more long, folded chains of amino acids (each called a polypeptide), whose sequences are determined by the DNA sequence of the protein-encoding gene.